What Health Conditions Are Common Causes of Hair Loss in Men and How They Impact Overall Well-being
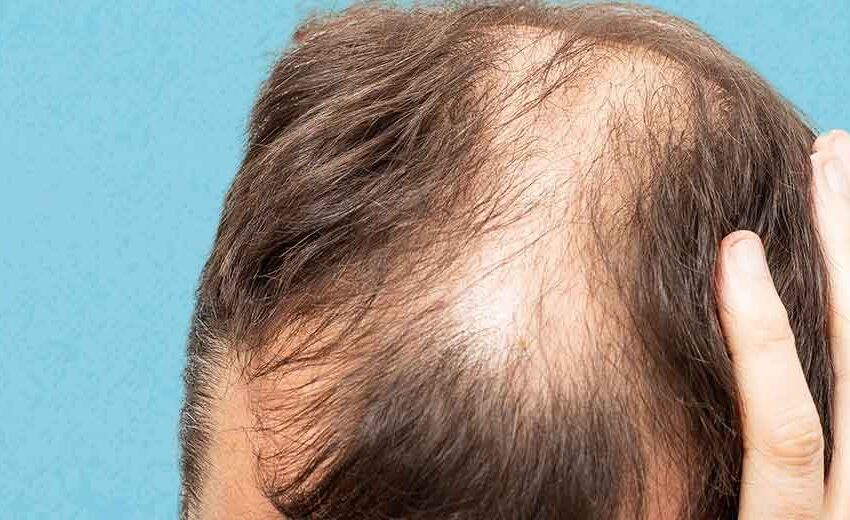
Many men worry about losing their hair, and it’s not just about age. Health conditions like thyroid disorders, anemia, and stress can cause noticeable hair thinning or bald spots. Sometimes, underlying issues such as hormonal changes or autoimmune diseases are the real reason behind the problem.
Some options can help slow hair loss and encourage new growth. There are plenty of choices for those looking to improve thinning or support regrowth, including specially formulated hair growth products for men. These can be used alongside treatments for the underlying health conditions to see better results.
Knowing what might be causing hair loss is an important first step. This helps men choose the right solution that matches their needs and health, rather than guessing or ignoring the signs.
Major Health Conditions That Cause Hair Loss in Men
Hair loss in men can happen for many reasons, but certain health problems are common causes. Genetics, hormone imbalances, and immune system issues often play a big role in why men lose hair.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia is the most frequent cause of hair loss in men. This condition happens when a man’s genes and hormones affect the hair follicles. The hairline usually starts to recede at the temples, and hair on the top of the head becomes thinner.
As this process goes on, men may notice a bald spot on the crown. In time, only a ring of hair along the sides and back of the scalp may remain. This type of hair loss often begins in the late teens or early twenties and gets worse with age.
Treatments such as medication, topical solutions, and hair transplant surgery are common options for men who want to slow the process or restore some of their hair.
Thyroid Disorders
Both overactive and underactive thyroid glands can cause hair loss in men. The thyroid makes hormones that keep many body functions working, including hair growth. When hormone levels are off, the hair growth cycle can be disrupted. This often results in thinning hair all over the scalp, instead of just in patches.
Symptoms of thyroid problems may include changes in weight, energy, and mood. Sometimes, treating the thyroid disease helps hair regrow. If the hormone imbalance continues, the hair loss may become long-term. Blood tests can help confirm thyroid disease, and doctors may suggest medicines to fix hormone levels and support hair regrowth.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases, such as alopecia areata, occur when the immune system attacks healthy hair follicles by mistake. This attack leads to sudden, patchy hair loss. In some cases, the hair may fall out in coin-sized areas or may even affect facial hair or other parts of the body.
Unlike pattern baldness, the hair can regrow on its own, but the condition might come and go. Other symptoms can include nail changes or tingling in the skin. Treatment for autoimmune hair loss can include steroid creams, injections, or other medicines that calm down the immune response. Early treatment can sometimes help slow new hair loss and help hair grow back.
Other Medical Causes and Related Factors
Hair loss in men isn’t always due to age or genetics. Sometimes, it can be linked to health problems, poor diet, or the side effects of treatments.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of important nutrients can cause thinning hair or even bald patches. Not getting enough iron or protein is a common issue linked with hair loss. Men who eat very little meat, follow strict diets, or skip meals frequently are more likely to notice their hair becoming thin.
Low levels of zinc, vitamin D, and certain B vitamins may also play a role in losing hair. These nutrients help hair stay healthy and strong. Without them, the body cannot produce hair as normal. A blood test can help show if these nutrients are low.
Some signs of nutrient deficiency might include tiredness, pale skin, or brittle nails in addition to losing hair. Addressing the underlying deficiency with foods or supplements often improves hair growth.
Chronic Illnesses
Medical conditions such as thyroid problems, diabetes, and anemia can all cause hair to thin or fall out. If the thyroid is not working right—either overactive or underactive—it often affects hair growth. Blood sugar that is too high or too low may also slow down hair production.
Autoimmune diseases sometimes make the body attack its own hair follicles, which leads to patches of hair loss. Conditions like lupus and alopecia areata are two examples. In cases of anemia, low red blood cell counts mean the hair gets less oxygen and nutrients.
Treating the medical condition often helps slow hair loss. If someone experiences sudden or patchy loss, it is important to get a medical checkup.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medicines can have hair loss as a side effect. This might include drugs for blood pressure, arthritis, depression, heart problems, or cancer. Chemotherapy, in particular, often causes sudden and widespread hair thinning.
Some treatments that adjust hormones, like those for prostate issues, can also impact hair growth. If new hair loss starts after beginning a medicine, the drug could be the cause.
Doctors may suggest changing the dose or switching medications, depending on the reason for hair loss. Usually, if the drug is stopped, hair often starts to grow back within a few months.
Conclusion
Hair loss in men is often linked to genetic factors, hormonal changes, and age. Some medical conditions and certain medications can also play a role.
Understanding the main causes can help people take steps to manage or slow down hair loss.
If someone is worried about hair loss, they should talk to a health professional to discuss possible reasons and solutions.
Early attention makes it easier to find helpful options.





